Data Integration
Data Modeling
Data Modeling
Data modeling is the art of defining the right representation and structure of data for the different architecture layers of an analytic solution.
The Faction A professionals have the skills and qualifications, both functional and technical, to define the modeling of data specific to the different layers of the analytical solution chosen architecture.
Our specialists possess knowledge and experience of the different analytical solutions data modeling techniques. Faction A has the know-how to deliver quality quickly according best practices.
The process
Depending on the architectural choices made, different models can be found, such as the staging, the data warehouse, the datamarts, the cubes.
You have to make good choices among the data modeling techniques. Depending on the architecture layers and the ways of storing the data, several techniques can be considered to structure the data and make it easily and quickly accessible.
The choices to be made on the different techniques:
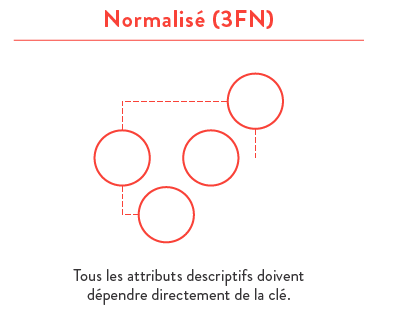
- third normal form (3NF);
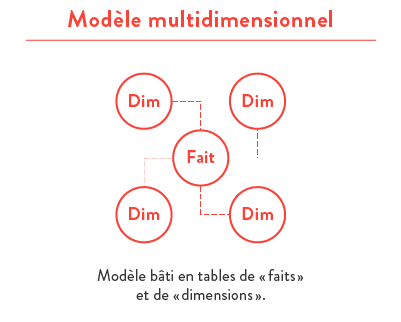
- multidimensional star schema modelisation;
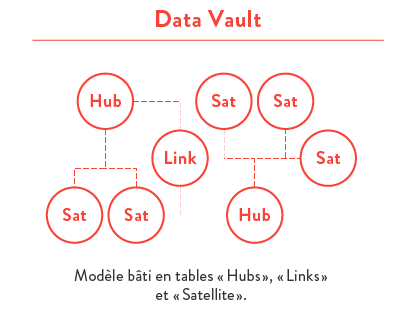
- or Data Vault 2.0.
Many factors need to be considered to establish the right choices, for example:
- the data history;
- the data volume and performance;
- the data versioning needs;
- the evolution capacity;
- the decommissioning of operational system, etc.
The use of the “Data Vault” modeling technique is becoming more and more widespread and ensures flexibility and an optimal solution. This approach also minimizes the impact and effort when changing business rules or the level of granularity required.
To establish good data structure, we must understand:
- the informational needs;
- the business rules and the underlying data;
- the granularity levels;
- the aggregate levels as well as the different architecture layers of the analytical solution.
We must capture and define:
- the good business concepts;
- the facts;
- the dimensions.
Standardise:
- the attributes;
- the master data;
- and the relations.
Application of specific elements for data loading, error handling, data integrity, unique record identification, key management, and versioning and time repository must be introduced to data modeling. In addition, it is at this point that the semantic definition of the elements is established.
Continuous workshops and revisions of the models with the different architects are required in order to carry out the required activities and this in an iterative and incremental delivery context where the modeling is detailed and implemented in a physical data model for priority needs.
Deliverables
1- One or many data models according to the architecture layers of the analytical solution.
2- Model(s) implémentation in targeted technologies.
Tools & Technologies
- Implementation of the model(s) in Microsoft storage engines such as Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Datawarehouse, Azure Data Lake Store, SQL Server.
- Graphic representation in tools such as Visio, Visual Studio Team Service (VSTS-Azure DEVOPS)
- Office and collaboration tools ex. Word, Excel, Microsoft Teams, Skype

